LeetCode-445. Add Two Numbers II
问题描述
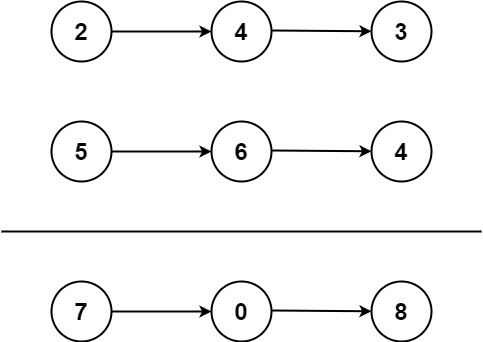
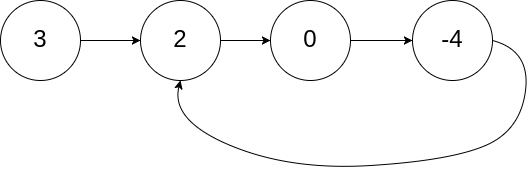
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The most significant digit comes first and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example :
1 | Input: l1 = [7,2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each linked list is in the range
[1, 100]. 0 <= Node.val <= 9- It is guaranteed that the list represents a number that does not have leading zeros.